Salivary and serum irisin in healthy adults before and after exercise
Accepted: 11 January 2023
HTML: 46
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
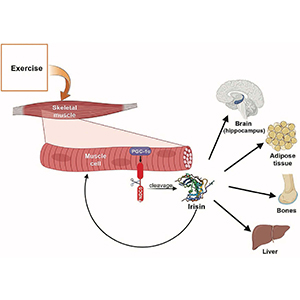
Irisin is an exercise-induced cytokine mainly secreted by myocytes. Circulating level of irisin can increase in response to acute exercise, promoting pleiotropic effects on health. Generally, irisin is evaluated in blood, however, its collection is invasive. Saliva sample would not have any risk associated with blood collection and would represent a less invasive method for irisin detection. Until now, there are only a few studies that have analyzed irisin levels in saliva. In the present research, five healthy male adults performed an incremental exercise until exhaustion on cycle ergometer. Serum and saliva samples were collected before exercise and 15min, 24h and 48h after reaching the exhaustion. Irisin was detected by ELISA assay. Serum and salivary irisin levels increased from baseline to 24h post exercise and reverted to basal levels after 48h of rest. A significant rise of both serum and salivary irisin level at 24h (p≤0.05) compared to baseline levels was found. Furthermore, a significant correlation between irisin percentage change in serum and saliva from baseline to 24h post exercise was detected (r=0.92, p<0.05). Despite the relatively limited sample, this research suggests that collecting saliva samples might represent a valid and less invasive method to detect irisin level changes induced by exercise.
Boström P, Wu J, Jedrychowski MP, Korde A, Ye L, Lo JC, Rasbach KA, Boström EA, Choi JH, Long JZ, Kajimura S, Zingaretti MC, Vind BF, Tu H, Cinti S, Højlund K, Gygi SP, Spiegelman BM. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 2012 Jan 11;481(7382):463-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10777
Liu S, Cui F, Ning K, Wang Z, Fu P, Wang D, Xu H. Role of irisin in physiology and pathology. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 26;13:962968. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.962968
Momenzadeh S, Jami MS, Jalalvand A, Esfarjani F, Shahabi S, Zamani S. Irisin, A Mediator of Muscle Crosstalk with Other Organs: From Metabolism Regulation to Protective and Regenerative Effects. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2022;23(2):89-104. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203723666220217141918
Pedersen BK, Febbraio MA. Muscles, exercise and obesity: skeletal muscle as a secretory organ. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012 Apr 3;8(8):457-65. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2012.49
Reza MM, Sim CM, Subramaniyam N, Ge X, Sharma M, Kambadur R, McFarlane C. Irisin treatment improves healing of dystrophic skeletal muscle. Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 6;8(58):98553-98566. DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21636
Reza MM, Subramaniyam N, Sim CM, Ge X, Sathiakumar D, McFarlane C, Sharma M, Kambadur R. Irisin is a pro-myogenic factor that induces skeletal muscle hypertrophy and rescues denervation-induced atrophy. Nat Commun. 2017 Oct 24;8(1):1104. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01131-0
Fox J, Rioux BV, Goulet EDB, Johanssen NM, Swift DL, Bouchard DR, Loewen H, Sénéchal M. Effect of an acute exercise bout on immediate post-exercise irisin concentration in adults: A meta-analysis. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018 Jan;28(1):16-28. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.12904
Williamson S, Munro C, Pickler R, Grap MJ, Elswick RK Jr. Comparison of biomarkers in blood and saliva in healthy adults. Nurs Res Pract. 2012;2012:246178. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/246178
Edgar WM. Saliva: its secretion, composition and functions. Br Dent J. 1992 Apr 25;172(8):305-12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bdj.4807861
Drobitch RK, Svensson CK. Therapeutic drug monitoring in saliva. An update. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1992 Nov;23(5):365-79. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199223050-00003
Yoshida Y, Yajima Y, Fujikura Y, Zhuang H, Higo-Yamamoto S, Toyoda A, Oishi K. Identification of salivary microRNA profiles in male mouse model of chronic sleep disorder. Stress. 2023 Jan;26(1):21-28. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10253890.2022.2156783
Aydin S, Aydin S, Kuloglu T, Yilmaz M, Kalayci M, Sahin I, Cicek D. Alterations of irisin concentrations in saliva and serum of obese and normal-weight subjects, before and after 45 min of a Turkish bath or running. Peptides. 2013 Dec;50:13-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2013.09.011
Aydin S, Aydin S, Kobat MA, Kalayci M, Eren MN, Yilmaz M, Kuloglu T, Gul E, Secen O, Alatas OD, Baydas A. Decreased saliva/serum irisin concentrations in the acute myocardial infarction promising for being a new candidate biomarker for diagnosis of this pathology. Peptides. 2014 Jun;56:141-5. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2014.04.002
Hirsch HJ, Gross I, Pollak Y, Eldar-Geva T, Gross-Tsur V. Irisin and the Metabolic Phenotype of Adults with Prader-Willi Syndrome. PLoS One. 2015 Sep 3;10(9):e0136864. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0136864
Bakal U, Aydin S, Sarac M, Kuloglu T, Kalayci M, Artas G, Yardim M, Kazez A. Serum, Saliva, and Urine Irisin with and Without Acute Appendicitis and Abdominal Pain. Biochem Insights. 2016 Jun 15;9:11-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4137/BCI.S39671
Altay DU, Korkmaz M, Ergun S, Korkmaz H, Noyan T. Salivary irisin: potential inflammatory biomarker in recurrent apthous stomatitis patients. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Mar;25(5):2252-2259.
Khan SU, Ghafoor S, Khaliq S, Syed AR. Salivary Irisin and periodontal clinical parameters in patients of chronic periodontitis and healthy individuals: A novel salivary myokine for periodontal disease. J Pak Med Assoc. 2022 Jan;72(1):27-33.
Jasim H, Carlsson A, Hedenberg-Magnusson B, Ghafouri B, Ernberg M. Saliva as a medium to detect and measure biomarkers related to pain. Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 19;8(1):3220. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21131-4
Aro K, Wei F, Wong DT, Tu M. Saliva Liquid Biopsy for Point-of-Care Applications. Front Public Health. 2017 Apr 11;5:77. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2017.00077
Gordon CC, Chumlea WC, Roche AF. Stature, recumbent length and weight. In: Lohman TG, Roche AF, Martorell R, eds. Anthropometric standardization reference manual. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics; 1988. pp 1-5.
Helmerhorst EJ, Oppenheim FG. Saliva: a dynamic proteome. J Dent Res. 2007 Aug;86(8):680-93. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/154405910708600802
Ravara B, Zampieri S, Kern H, Carraro U. Blood contamination, a problem or a lucky chance to analyze non-invasively Myokines in mouth fluids? Eur J Transl Myol. 2019 Dec 10;29(4):8713. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2019.8713
Polyzos SA, Mantzoros CS. An update on the validity of irisin assays and the link between irisin and hepatic metabolism. Metabolism. 2015 Sep;64(9):937-42. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2015.06.005
Zhang Y, Li R, Meng Y, Li S, Donelan W, Zhao Y, Qi L, Zhang M, Wang X, Cui T, Yang LJ, Tang D. Irisin stimulates browning of white adipocytes through mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 MAP kinase and ERK MAP kinase signaling. Diabetes. 2014 Feb;63(2):514-25. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2337/db13-1106
Copyright (c) 2023 the Author(s)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.


 https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2023.11093
https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2023.11093



