Epidural and subdural hematoma following spinal anesthesia in infants rat model
Accepted: 26 August 2022
HTML: 27
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
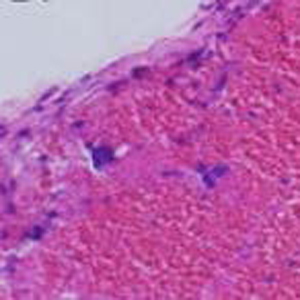
The aim of this study was to assess the epidural and subdural hematoma following spinal anesthesia in infants’ rat model. We investigated during 10, 15, and 20 days’ rats in group 1: intrathecal injection of bupivacaine 3.75 mg/kg (n = 7); group 2: received 37.5 μl midazolam 0.1% intrathecal with 37.5μl fentanyl 0.005% (no=7); injected into group 3 methylene blue 1 mg/ml (No. 7). Rats were exposed to spinal anesthesia in infancy and rotarod in motor function in adulthood. Histological evaluation and tissue extraction were also performed after the treatment and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the head. MRI of the head of all rat pups that showed similar symptoms were performed. 4 rat pups showed the symptoms of hematoma Group1: small acute subdural hematoma at the left posterior temporal-parietal junction (PTPJ) and group 2 (one: right temporal epidural hematoma, two: Small acute subdural hematoma in the right temporomandibular area, and three: frontal-temporal-parietal-occipital hematoma). the rat pup that had epidural hematoma died 6 hours later. Finally, in the first group, one rat and the second group three rats showed hematoma symptoms. For these three rats, a histopathologic study was performed and indicate the presence of small acute subdural hematoma at the left posterior temporal-parietal junction, right temporal epidural hematoma, and frontal-temporal-parietal-occipital hematoma. In summary, because subdural or epidural hematoma of the skull can have serious consequences, differential diagnosis is very important for pain after spinal anesthesia.
Su TM, Lee TH, Chen WF, Lee TC, Cheng CH. Contralateral acute epidural hematoma after decompressive surgery of acute subdural hematoma: clinical features and outcome. J Trauma. 2008 Dec;65(6):1298-302. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e31815885d9
Mahmood A, Roberts I, Shakur H. A nested mechanistic sub-study into the effect of tranexamic acid versus placebo on intracranial haemorrhage and cerebral ischaemia in isolated traumatic brain injury: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial (CRASH-3 Trial Intracranial Bleeding Mechanistic Sub-Study [CRASH-3 IBMS]). Trials. 2017 Jul 17;18(1):330. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-017-2073-6
Pierre L, Kondamudi NP. Subdural hematoma. InStatPearls [Internet] 2021 Sep 4. StatPearls Publishing.
Byyny RL, Mower WR, Shum N, Gabayan GZ, Fang S, Baraff LJ. Sensitivity of noncontrast cranial computed tomography for the emergency department diagnosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Ann Emerg Med. 2008 Jun;51(6):697-703. Epub 2008 Jan 22. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2007.10.007
Suwatcharangkoon S, Meyers E, Falo C, Schmidt JM, Agarwal S, Claassen J, Mayer SA. Loss of Consciousness at Onset of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage as an Important Marker of Early Brain Injury. JAMA Neurol. 2016 Jan;73(1):28-35. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.3188
Badjatia N, Carney N, Crocco TJ, Fallat ME, Hennes HM, Jagoda AS, Jernigan S, Letarte PB, Lerner EB, Moriarty TM, Pons PT, Sasser S, Scalea T, Schleien CL, Wright DW; Brain Trauma Foundation; BTF Center for Guidelines Management. Guidelines for prehospital management of traumatic brain injury 2nd edition. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2008;12 Suppl 1:S1-52. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10903120701732052
Zubkov AY, Lewis AI, Raila FA, Zhang J, Parent AD. Risk factors for the development of post-traumatic cerebral vasospasm. Surg Neurol. 2000 Feb;53(2):126-30. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0090-3019(99)00178-0
Colombari M, Troakes C, Turrina S, Tagliaro F, De Leo D, Al-Sarraj S. Spinal cord injury as an indicator of abuse in forensic assessment of abusive head trauma (AHT). Int J Legal Med. 2021 Jul;135(4):1481-1498. Epub 2021 Feb 22. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-021-02526-x
Firsching R. Coma After Acute Head Injury. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2017 May 5;114(18):313-320. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2017.0313
Pinto PS, Meoded A, Poretti A, Tekes A, Huisman TA. The unique features of traumatic brain injury in children. review of the characteristics of the pediatric skull and brain, mechanisms of trauma, patterns of injury, complications, and their imaging findings--part 2. J Neuroimaging. 2012 Apr;22(2):e18-41. Epub 2012 Feb 3. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1552-6569.2011.00690.x
Rabelo NN, Matushita H, Cardeal DD. Traumatic brain lesions in newborns. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2017 Mar;75(3):180-188. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/0004-282x20170016
Eikaas H, Raeder J. Total intravenous anaesthesia techniques for ambulatory surgery. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2009 Dec;22(6):725-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/ACO.0b013e3283310f6b
Sasaki Russell JM, Chinn GA, Maharjan D, Eichbaum Y, Sall JW. Female rats are more vulnerable to lasting cognitive impairment after isoflurane exposure on postnatal day 4 than 7. Br J Anaesth. 2019 Apr;122(4):490-499. Epub 2019 Jan 31. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bja.2018.12.008
Carlson SJ, Fallon EM, Kalish BT, Gura KM, Puder M. The role of the ω-3 fatty acid DHA in the human life cycle. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2013 Jan;37(1):15-22. Epub 2012 Nov 27. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0148607112467821
Semple BD, Blomgren K, Gimlin K, Ferriero DM, Noble-Haeusslein LJ. Brain development in rodents and humans: Identifying benchmarks of maturation and vulnerability to injury across species. Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Jul-Aug;106-107:1-16. Epub 2013 Apr 11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.04.001
Kwak KH. Postdural puncture headache. Korean journal of anesthesiology. 2017; 70(2):136-43. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4097/kjae.2017.70.2.136
Erbay RH, Senoglu N, Atalay H. Spinal or epidural haematoma. Topics in Spinal Anaesthesia. 2014 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5772/58702
Chien GC, McCormick Z, Araujo M, Candido KD. The potential contributing effect of ketorolac and fluoxetine to a spinal epidural hematoma following a cervical interlaminar epidural steroid injection: a case report and narrative review. Pain Physician. 2014 May-Jun;17(3):E385-95. DOI: https://doi.org/10.36076/ppj.2014/17/E385
Whedon JM, Quebada PB, Roberts DW, Radwan TA. Spinal epidural hematoma after spinal manipulative therapy in a patient undergoing anticoagulant therapy: a case report. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2006 Sep;29(7):582-5. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmpt.2006.06.017
Olutoye OA, Baker BW, Belfort MA, Olutoye OO. Food and Drug Administration warning on anesthesia and brain development: implications for obstetric and fetal surgery. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Jan;218(1):98-102. Epub 2017 Sep 6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2017.08.107
Davoudi M, Tarbiat M, Ebadian MR, Hajian P. Effect of Position During Spinal Anesthesia on Postdural Puncture Headache After Cesarean Section: A Prospective, Single-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. Anesth Pain Med. 2016 Jul 4;6(4):e35486. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5812/aapm.35486
Soliman HM, Arnold PM, Madarang EJ. Post-myelography paraplegia in a woman with thoracic stenosis. The journal of spinal cord medicine. 2013; 36(3):247-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1179/2045772313Y.0000000111
Peralta F, Devroe S. Any news on the postdural puncture headache front? Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2017 Mar;31(1):35-47. Epub 2017 Apr 15. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpa.2017.04.002
Bezov D, Lipton RB, Ashina S. Post-dural puncture headache: part I diagnosis, epidemiology, etiology, and pathophysiology. Headache. 2010 Jul;50(7):1144-52. Epub 2010 Jun 1. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01699.x
O'Connell TX. USMLE Step 2 Secrets E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2021 Oct 15.
Zahl SM, Mack JA, Rossant C, Squier W, Wester K. Thrombosis is not a marker of bridging vein rupture in infants with alleged abusive head trauma. Acta Paediatr. 2021 Oct;110(10):2686-2694. Epub 2021 May 20. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.15908
Kale A, Emmez H, Pişkin Ö, Durdağ E. Postdural puncture subdural hematoma or postdural puncture headache?: two cases report. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2015 Oct;68(5):509-12. Epub 2015 Sep 30. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4097/kjae.2015.68.5.509
Thorsen, G. Neurological complications after spinal anaesthesia and result, from 2493 folow-up cases. ActaChirScand, 1948; 137(14): 1262. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1948.02890480082028
Vaughan DJ, Stirrup CA, Robinson PN. Cranial subdural haematoma associated with dural puncture in labour. Br J Anaesth. 2000 Apr;84(4):518-20. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.bja.a013483
Yokota H, Miyamoto K, Yokoyama K, Noguchi H, Uyama K, Oku M. Spontaneous acute subdural haematoma and intracerebral haemorrhage in patient with HELLP syndrome: case report. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2009 Dec;151(12):1689-92. Epub 2009 Apr 24. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-009-0300-y
Domenicucci M, Ramieri A, Paolini S, Russo N, Occhiogrosso G, Di Biasi C, Delfini R. Spinal subarachnoid hematomas: our experience and literature review. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2005 Jul;147(7):741-50; discussion 750. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-004-0458-2
Borger V, Vatter H, Oszvald Á, Marquardt G, Seifert V, Güresir E. Chronic subdural haematoma in elderly patients: a retrospective analysis of 322 patients between the ages of 65-94 years. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2012 Sep;154(9):1549-54. Epub 2012 Jul 8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-012-1434-x
Bower JE. Behavioral symptoms in patients with breast cancer and survivors. J Clin Oncol. 2008 Feb 10;26(5):768-77. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2007.14.3248
Seraji-Bzorgzad N, Paulson H, Heidebrink J. Neurologic examination in the elderly. Handb Clin Neurol. 2019;167:73-88. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-804766-8.00005-4
Katirji B. Clinical assessment in neuromuscular disorders. InNeuromuscular disorders in clinical practice 2014 (pp. 3-20). Springer, New York, NY. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-6567-6_1
Oh JW, Kim SH, Whang K. Traumatic Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak: Diagnosis and Management. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2017 Oct;13(2):63-67. Epub 2017 Oct 31. DOI: https://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2017.13.2.63
Marigold R, Günther A, Tiwari D, Kwan J. Antiepileptic drugs for the primary and secondary prevention of seizures after subarachnoid haemorrhage. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jun 5;2013(6):CD008710. CD008710.pub2. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD008710.pub2
Copyright (c) 2022 The Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.


 https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2022.10778
https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2022.10778



