Total phenolic and flavonoids contents and in vitro evaluation of antioxidant activity of several Calendula officinalis (Marigold) extracts
Accepted: April 22, 2021
Appendix: 93
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
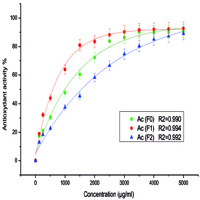
The search for natural antioxidants to replace synthetic antioxidants is one of humanity’s health priorities. Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (MAP) contain phenolic compounds that act as natural antioxidants. The aim of this work is to study total phenols and flavonoids contents and evaluate the antioxidant power of various extracts of Calendula officinalis. Extracts were prepared in two steps: hot solid-liquid extraction, by Soxhlet and from the plant powder using a solvent (Methanol/water 70/30, Acetone/water 70/30) followed by a liquid-liquid extraction by splitting the obtained extract by two increasingly polarized solvents (Ethyl acetate and Butanol). Total phenols and flavonoids were evaluated using gallic acid and quercetin as standards, respectively. The antioxidant activity of extracts was determined by DPPH (2,2-diphényl 1-picrylhydrazyle) free radical reduction method. The two crude fractions of Methanol and Acetone presented the highest levels of total phenols (7,58±0,38 mg GAE/g dm and 6,80±0,34 mg GAE/g dm respectively), and flavonoids (7,37±0,37 mg QE/g dm and 7,93±0,40 mg QE/g dm respectively). Ethyl acetate fractions showed a high antioxidant activity. This study demonstrated that extracts from Calendula officinalis flowers present a promising source of natural antioxidant.
Panda SK. Assay Guided Comparison for Enzymatic and Non-Enzymatic Antioxidant Activities with Special Reference to Medicinal Plants. In: Antioxidant Enzyme. 2012. p. 381–400.
Agati G, Azzarello E, Pollastri S, Tattini M. Flavonoids as antioxidants in plants: Location and functional significance. Plant Sci 2012 Nov 1;196:67–76. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2012.07.014
Cao G, Sofic E, Prior RL. Antioxidant Capacity of Tea and Common Vegetables. J Agric Food Chem 1996;44:3426–31. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9602535
Shebis Y, Iluz D, Kinel-Tahan Y, et al. Natural Antioxidants: Function and Sources. Food Nutrition Sci 2013;04:643. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4236/fns.2013.46083
Aubin F. Rayonnement ultraviolet et peau. John Libbey Eurotext. 2001. Accessed: 2018 May 2. Available from: http://www.jle.com/fr/ouvrages/e-docs/rayonnement_ultraviolet_et_peau_20172/ouvrage.phtml
Varka E-M, Tsatsaroni E, Xristoforidou N, Darda A-M. Stability Study of O/W Cosmetic Emulsions Using Rosmarinus officinalis and Calendula officinalis Extracts. Open J Appl Sci 2012;02:139–45. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4236/ojapps.2012.23020
Butnariu M, Coradini CZ. Evaluation of biologically active compounds from calendula officinalis flowers using spectrophotometry. Chem Central J 2012;6:35. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-153X-6-35
Kalvatchev Z, Walder R, Garzaro D. Anti-HIV activity of extracts from Calendula officinalis flowers. Biomed Pharmacother 1997;51:176–80. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0753-3322(97)85587-4
Isaac O. Die Ringelblume: Botanik, Chemie, Pharmakologie, Toxikologie, Pharmazie und therapeutische Verwendung. Stuttgart: Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft; 1992: p. 787.
Akhtar N. Evaluation of various functional skin parameters using a topical cream of Calendula officinalis extract. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol 2011;5:199–206. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR10.368
Barnes J, Anderson LA, Phillpson JD. Herbal Medicines. Pharmaceutical Press: London; 2002.
Hall RL, Oser BL. Recent progress in the consideration of flavoring ingredients under the Food Additives Amendment. 3. gRAS substances. Food Technol 1965;19. Available from: http://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=US201302362835
Fierascu I, Bunghez I-R, Fierascu C, Ion R-M, Dinu-pîrvu E, Ni D. Characterization and antioxidant activity of phytosynthesised silver nanoparticles using calendula officinalis extract. Farmacia 2014;62:8.
Preethi KC, Kuttan G, Kuttan R. Antioxidant potential of an extract of Calendula officinalis. Flowers in vitro and in vivo. Pharmaceut Biol 2006;44:691–7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/13880200601009149
Velickovic J, Dimitrijevic D, Mitic S, et al. The determination of the phenolic composition, antioxidative activity and heavy metals in the extracts of Calendula officinalis L. Savremene Tehnologije 2014;3:46–51. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5937/savteh1402046V
Herold A, Cremer L, Calugăru A, et al. Antioxidant properties of some hydroalcoholic plant extracts with antiinflammatory activity. Roum Arch Microbiol Immunol 2003;62:217–27.
Bammou M, Daoudi A, Sellam K, [ Ethnobotanical Survey of Asteraceae Family used in Meknes-Tafilalet Region (Morocco)]. Int J Innovation Appl Studies 2015;13:789‐815.
El Amri J, El Badaoui K, Zair T, Bouharb H. Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants in the region El Hajeb (central Morocco). J Research Biol 2014;4:1568–80.
Bruneton J. Pharmacognosie: Phytochimie, Plantes médicinales. 4e édition. Cachan: Tec & Doc Lavoisier; 2009.
N’Guessan K, Kadja B, Zirihi G, et al. Screening phytochimique de quelques plantes médicinales ivoiriennes utilisées en pays Krobou (Agboville, Côte-d’Ivoire). Sci Nature 2009;6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4314/scinat.v6i1.48575
Singleton VL, Orthofer R, Lamuela-Raventós RM. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of folin-ciocalteu reagent. In: Methods in Enzymology. Oxidants and Antioxidants, Part A. Academic Press; 1999: p. 152–78. Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0076687999990171 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(99)99017-1
Kosalec I, Bakmaz M, Pepeljnjak S, Vladimir-Knezević S. Quantitative analysis of the flavonoids in raw propolis from northern Croatia. Acta Pharm 2004;54:65–72.
Alnuqaydan A, Lenehan C, Hughes R, J. Sanderson B. Extracts from Calendula officinalis Offer in Vitro Protection Against H2O2 Induced Oxidative Stress Cell Killing of Human Skin Cells. Phytother Res 2014;29. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5236
Muley B, Khadabadi S, Banarase N. Phytochemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Calendula officinalis Linn (Asteraceae): A review. Tropic J Pharmaceut Res 2009;8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v8i5.48090
Pietta P, Bruno A, Mauri P, Rava A. Separation of flavonol-2-O-glycosides from Calendula officinalis and Sambucus nigra by high-performance liquid and micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography. J Chromatography A 1992;593:165–70. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9673(92)80282-Y
Cetkovic G, Djilas S, Canadanovic-Brunet J, Tumbas V. Thin-layer chromatography analysis and scavenging activity of marigold (Calendula officinalis L) extracts. Acta Periodica Technologica 2003;34:93–102. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2298/APT0334093C
Elazzouzi H, Zekri N, Zair T, Alaoui El Belghiti M. Total phenolic and flavonoid contents of Anacyclus pyrethrum Link plant extracts and their Antioxidant activity. Karbala Int J Modern Sci 2019;5:10. DOI: https://doi.org/10.33640/2405-609X.1269
Deliorman Orhan D, Hartevioğlu A, Küpeli E, Yesilada E. In vivo anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activity of the crude extract and fractions from Rosa canina L. fruits. J Ethnopharmacol 2007;112:394–400. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2007.03.029
Wei L, Yanxiang G, Jian Z, Qi W. Phenolic, flavonoid, and lutein ester content and antioxidant activity of 11 cultivars of Chinese marigold. J Agricult Food Chem 2007;8478–84. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jf071696j
Ahmad H, Khan I, Wahid A. Antiglycation and antioxidation properties of Juglans regia and Calendula officinalis: possible role in reducing diabetic complications and slowing down ageing. J Trad Chinese Med 2012;32:411–4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0254-6272(13)60047-3
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.


 https://doi.org/10.4081/jbr.2021.9680
https://doi.org/10.4081/jbr.2021.9680



