The protective effect of Matricaria pubescens extracts against alloxan-induced hyperglycemia in rats
Accepted: July 30, 2022
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
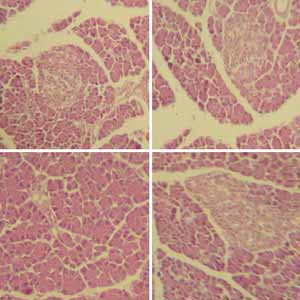
The purpose of this research is to look into the potential inhibitory capacity of Matricaria pubescens methanolic extract (EMMP) on key diabetes-related enzymes in diabetic rats. A significant increase in serum and pancreatic α-amylase activity in untreated diabetic rats (Diab) of 61% and 75%, respectively, resulted in an 184% increase in blood glucose levels compared to controls. However, compared to untreated diabetic rats, treatment with the extract (Diab + EMMP) resulted in a significant decrease in pancreatic α-amylase activity in the pancreas (15%) and serum (28%). As a result, a significant reduction in blood sugar level has been observed, reaching 28%. When rats treated with EMMP were compared to untreated diabetics, the level of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) decreased by 28%. Furthermore, a significant increase in pancreatic serum lipase activity (59%) in untreated diabetic rats treated with EMMP resulted in a significant inhibition (21%). In diabetic rats treated with EMMP, β-cells were found to have a powerful protective effect. However, we observed body weight recovery in diabetic rats treated with EMMP.
Pan S, Zhou D, Gao S. New perspectives on how to discover drugs from herbal medicines: cam's outstanding contribution to modern therapeutics. Evid Based Complement Altern Med 2013;2013:1–25.
Othman AI, El-Sawi MR, El-Missiry MA, et al. Epigallocatechin-3 gallate protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy through modulating the cardio metabolic risk factors, oxidative stress, inflammation, cell death and fibrosis in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother 2017;94:362-73.
American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2009;32:S62–7.
Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, et al. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 2004;27:1047-53.
Boadu AA, Asase A. Documentation of herbal medicines used for the treatment and management of human diseases by some communities in Southern Ghana. Evid Based Complement Altern Med 2017;2017:1-12.
Hammiche V, Maiza K. Traditional medicine in Central Sahara: Pharmacopoeia of Tassili N’ajjer. J Ethnopharmacol 2006;105:358-67.
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 1972;18:499-502.
Hamden K, Jaouadi B, Carreau S, et al. Therapeutic effects of soy isoflavones on alpha-amylase activity, insulin deficiency, liver-kidney function and metabolic disorders in diabetic rats. Nat Prod Res 2011;25:244-55.
Kamboj A, Kumar S, Kumar V. Evaluation of Antidiabetic Activity of Hydroalcoholic Extract of Cestrum nocturnum Leaves in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Adv Pharmacol Sci 2013;1013:150401.
Gabe M. Techniques histologiques. Massie e Cie, Paris, 1968;113p
Ajiboye BO, Ojo OA, Akuboh OS, et al. Anti-hyperglycemic and anti-inflammatory activities of polyphenolic-rich extract of Syzygium cumini Linn leaves in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. J Evid Based Integr Med 2018;23:2515690X18770630.
Boukhris M, Regane G, Yangui T, et al. Chemical composition and biological potential of essential Oil from Tunisian Cupressus sempervirens L. J Arid Land 2012;22:329-32.
Elekofehinti O, Kamdemj P, Bolingon AA, et al. African eggplant (Solanum anguivi Lam.) fruit with bioactive polyphenolic compounds exerts in vitro antioxidant properties and inhibits Ca2+ induced mitochondrial swelling. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2013;3:757-66.
Mnafgui K, Kaanich F, Derbali A. Inhibition of key enzymes related to diabetes and hypertension by eugenol in vitro and in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Arch Physiol Biochem 2013;119:225-33.
Chen V, Ianuzzo CD. Dosage effect of streptozotocin on rat tissue enzyme activities and glycogen concentration. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 1982;60:1251-6.
Veeramani C, Pushpavalli G, Pugalendi KV. Antihyperglycaemic effect of Cardiospermum halicacabum Linn. Leaf extract on STZ-induced diabetic rats. J Appl Biomed 2008;6:19-26.
Mnafgui K, Kchaou M, Hamden K, et al. Inhibition of carbohydrate and lipid digestive enzymes activities by Zygophyllum album extracts: effect on blood and pancreas inflammatory biomarkers in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. J Physiol Biochem 2014;70:93-106.
Aloulou A, Hamden K, Elloumi D, et al. Hypoglycemic and antilipidemic properties of kombucha tea in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 2012;12:63
Srinivasan S, Muthukumaran J, Muruganathan U, et al. Antihyperglycemic effect of syringic acid on attenuating the key enzymes of carbohydrate metabo-lism in experimental diabetic rats. Biomed Prevent Nut 2014;4:595-602
Bayramoglu A, Bayramoglu G, Senturk H. Lycopene partially reverses symptoms of diabetes in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J Med Food 2013;16:128-32.
Kamrani YY, Amanlou M, Yazdanyar A, et al. Potential anti-diabetic and anti-oxidant activity of essential oil of Zataria multiflora leaves. Planta Med 2008;74:PA72
Prabhakar PK, Doble M. Interaction of phytochemicals with hypoglycemic drugs on glucose uptake in L6 myotubes. Phytomedicine 2011;18:285-91.
Palsamy P, Subramanian S. Resveratrol, a natural phytoalexin, normalizes hyperglycemia in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced experimental diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother 2008;62:598-605.
Zhang X, Shi Z, Liu Q, et al. Effects of coenzyme Q10 intervention on diabetic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2019;98:e15850.
Aba PE, Asuzu IU. Mechanisms of actions of some bioactive anti-diabetic principles from phytochemicals of medicinal plants: a review. Indian J Nat Prod Resour 2018;9:85-96.
Rajasekaran A, Kalaivani M. Designer foods and their benefits: A review. J Food Sci Technol 2013;50:1-16.
Mnafgui K, Hamden K, Ben Salah H, et al. Inhibitory Activities of Zygophyllum album: A Natural Weight-lowering Plant on Key Enzymes in High-fat Diet-fed Rats. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med 2012;10:384–92.
Copyright (c) 2022 the Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.


 https://doi.org/10.4081/jbr.2022.10441
https://doi.org/10.4081/jbr.2022.10441



