Anaemia, thrombocytopenia and skin lesions
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
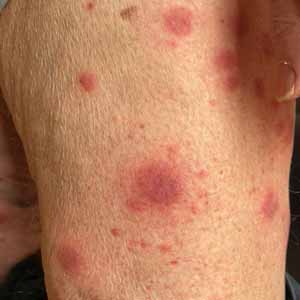
A 73-year-old man affected by hyperuricemia, dyslipidaemia and hypothyroidism presented to the emergency room with a 3-month history of fever, exertional dyspnea, progressive asthenia, and painless not itchy skin lesions. Physical exam showed purplish papules and plaques affecting any area of his body, and a slight bilateral oedema of his legs. Laboratory studies revealed a severe macrocytic anaemia (haemoglobin 4.8 g/dL, mean cell volume 119 fL) and thrombocytopenia (34,000/mm3) with hyperferritinemia (1894 ng/mL, normal value <400) and increased serum B12 (1412 pg/mL, normal value 197-771), associated with ESR 71 mm/h (normal value 1-15), CRP 139 mg/L (normal value <6), and procalcitonin 1.05 ng/mL (normal value <0.5).
Anhalt GJ, Kim SC, Stanley JR, et al. Paraneoplastic pemphigus. An autoimmune mucocutaneous disease associated with neoplasia. N Engl J Med 1990;323:1729-35. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199012203232503
Ohzono A, Sogame R, Li X, et al. Clinical and immunological findings in 104 cases of paraneoplastic pemphigus. Br J Dermatol 2015;173:1447–52. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.14162
Lim JM, Lee SE, Seo J, et al. Paraneoplastic pemphigus associated with a malignant thymoma: a case of persistent and refractory oral ulcerations following thymectomy. Ann Dermatol 2017;29:219–22. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.2.219
Lee SE, Kim SC. Paraneoplastic pemphigus. Dermatol Sinica 2010;28:1–14. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1027-8117(10)60001-8
Lee J, Bloom R, Amber KT. A systematic review of patients with mucocutaneous and respiratory complications in paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome: castleman’s disease is the predominant malignancy. Lung 2015;193:593–6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-015-9732-8
Kim JH, Kim SC. Paraneoplastic Pemphigus: Paraneoplastic Autoimmune Disease of the Skin and Mucosa. Front Immunol 2019;10:1259. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01259
Chin AC, Stich D, White FV, et al. Paraneoplastic pemphigus and bronchiolitis obliterans associated with a mediastinal mass: a rare case of Castleman’s disease with respiratory failure requiring lung transplantation. J Pediatr Surg 2001;36:E22. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1053/jpsu.2001.28877
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.


 https://doi.org/10.4081/ecj.2022.10498
https://doi.org/10.4081/ecj.2022.10498







