Understanding the influence of high novelty-seeking on academic burnout: Moderating effect of physical activity
HTML: 30
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
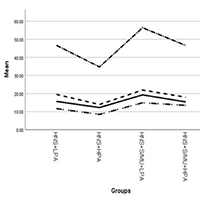
A large number of studies have shown a positive correlation between high novelty-seeking (HNS), substance/medication use (S/MU), high physical activity (HPA), and academic burnout (AB); however, the outcome of individuals with HNS in the terms of catching AB is doubtful. The present study was conducted to find out whether the personality traits such as HNS in medical students predisposes the AB or decreases its severity by increased physical activity (PA). This cross-sectional study, 227 medical students with HNS were selected from three major cities of Iran during February, 2019 to July, 2019 using convenience sampling and were assessed using demographic information form, Baecke’s physical activity questionnaire, and Breso’s academic burnout questionnaire. In this study, 126 male and 151 female participants were divided into four groups namely HNS + low physical activity (LPA) (n = 68); HNS + HPA (n = 73); HNS + S/MU + LPA (n = 72); and HNS + S/MU + HPA (n = 64). The study results indicated that the maximum and minimum mean scores of AB and its subscales were in the HNS + S/MU + LPA and HNS + HPA groups, respectively. In addition, the hierarchical multiple regression analysis results for the two groups of students with and without S/MU indicated that PA plays a moderating role in the relationship between AB and HNS. Given that the AB can be considered as an antecedent of depressive disorders, its lowered level could be effective in preventing major depressive disorder. Regarding the moderating role of PA in the relationship between HNS and AB, PA, as a relatively simple and inexpensive alternative to pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy, can be raised in the treatment and prevention of the AB.
Lee SJ, Choi YJ, Chae H. The effects of personality traits on academic burnout in Korean medical students. Integrative medicine research. 2017 Jun 1;6(2):207-13. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imr.2017.03.005
Freudenberger HJ. Staff burn‐out. Journal of social issues. 1974 Jan;30(1):159-65. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-4560.1974.tb00706.x
Maslach C, Jackson SE. The measurement of experienced burnout. Journal of organizational behavior. 1981 Apr;2(2):99-113. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/job.4030020205
Jacobs SR, Dodd D. Student burnout as a function of personality, social support, and workload. Journal of college student development. 2003;44(3):291-303. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1353/csd.2003.0028
Cloninger CR, Svrakic DM, Przybeck TR. A psychobiological model of temperament and character. The development of psychiatry and its complexity. 1998;50(12):1-6.
Zuckerman M, Kuhlman DM, Joireman J, Teta P, Kraft M. A comparison of three structural models for personality: the big three, the big five, and the alternative five. Journal of personality and social psychology. 1993 Oct;65(4):757. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.65.4.757
Wingo T, Nesil T, Choi JS, Li MD. Novelty seeking and drug addiction in humans and animals: from behavior to molecules. Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology. 2016 Sep 1;11(3):456-70. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-015-9636-7
Khan AA, Jacobson KC, Gardner CO, Prescott CA, Kendler KS. Personality and comorbidity of common psychiatric disorders. The British Journal of Psychiatry. 2005 Mar;186(3):190-6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.186.3.190
Jackson ER, Shanafelt TD, Hasan O, Satele DV, Dyrbye LN. Burnout and alcohol abuse/dependence among US medical students. Academic Medicine. 2016 Sep 1;91(9):1251-6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/ACM.0000000000001138
Flagel SB, Waselus M, Clinton SM, Watson SJ, Akil H. Antecedents and consequences of drug abuse in rats selectively bred for high and low response to novelty. Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan 1;76:425-36. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.033
Finn PR, Mazas CA, Justus AN, Steinmetz J. Early‐onset alcoholism with conduct disorder: go/no go learning deficits, working memory capacity, and personality. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 2002 Feb;26(2):186-206. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2002.tb02524.x
Brunes A, Augestad LB, Gudmundsdottir SL. Personality, physical activity, and symptoms of anxiety and depression: the HUNT study. Social psychiatry and psychiatric epidemiology. 2013 May 1;48(5):745-56. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-012-0594-6
Rhodes RE, Smith NE. Personality correlates of physical activity: a review and meta-analysis. British journal of sports medicine. 2006 Dec 1;40(12):958-65. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsm.2006.028860
Yazici AB, Esen O, Yazici E, Esen H, Ince M. The relationship between temperament and character traits and burnout among nurses. Journal of Psychology & Psychotherapy. 2014 Jan 1;4(5):1-5.
Stevens JP. Multiple regression. In Applied multivariate statistics for the social sciences 2012 Nov 12 (pp. 75-156). Routledge. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203843130-7
Abuzar Soury, Keivan Shabani Moghadam, Rabiallah Soury. The Effect of physical activity on quality of life in elder women in Kermanshah Province. Applied Research of Sport Management Vol.4, no.4, Spring 2016. (Persian)
Dadfar M, Bahrami F, Dadfar F, Younesi S J. Reliability and Validity of the Temperament and Character Inventory. jrehab. 2010; 11(3): 15-24. (Persian)
Naami AA. Relationship between quality of learning experiences and academic burnout in graduate students of Shahid Chamran University. Psychological Studies J. 2009;5(3):117-134. (Persian)
Gerber M, Brand S, Elliot C, Holsboer-Trachsler E, Pühse U, Beck J. Aerobic exercise training and burnout: a pilot study with male participants suffering from burnout. BMC Research Notes. 2013 Dec;6(1):78. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-6-78
Brand S, Gerber M, Beck J, Hatzinger M, Pühse UW, Holsboer-Trachsler E. Exercising, sleep-EEG patterns, and psychological functioning are related among adolescents. The World Journal of Biological Psychiatry. 2010 Jan 1;11(2):129-40. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3109/15622970903522501
Shirom A, Melamed S, Toker S, Berliner S, Shapira I. Burnout and health review: Current knowledge and future research directions. International review of industrial and organizational psychology. 2005 Dec 13;20(1):269-308. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/0470029307.ch7
Parker G, Crawford J. Judged effectiveness of differing antidepressant strategies by those with clinical depression. Australian and New Zealand journal of psychiatry. 2007 Jan 1;41(1):32-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00048670601057726
Lindwall M, Ljung T, Hadžibajramović E, Jonsdottir IH. Self-reported physical activity and aerobic fitness are differently related to mental health. Mental Health and Physical Activity. 2012 Jun 1;5(1):28-34. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mhpa.2011.12.003
Toker S, Biron M. Job burnout and depression: unraveling their temporal relationship and considering the role of physical activity. Journal of Applied Psychology. 2012 May;97(3):699. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1037/a0026914
Jonsdottir IH, Rödjer L, Hadzibajramovic E, Börjesson M, Ahlborg Jr G. A prospective study of leisure-time physical activity and mental health in Swedish health care workers and social insurance officers. Preventive medicine. 2010 Nov 1;51(5):373-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2010.07.019
Schaufeli W, Enzmann D. The burnout companion to study and practice: A critical analysis. CRC press; 1998 Nov 17.
Suls J, Bunde J. Anger, anxiety, and depression as risk factors for cardiovascular disease: the problems and implications of overlapping affective dispositions. Psychological bulletin. 2005 Mar;131(2):260. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.131.2.260
Beck AT, Steer RA, Carbin MG. Psychometric properties of the Beck Depression Inventory: Twenty-five years of evaluation. Clinical psychology review. 1988 Jan 1;8(1):77-100. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0272-7358(88)90050-5
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.


 https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2020.8722
https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2020.8722



